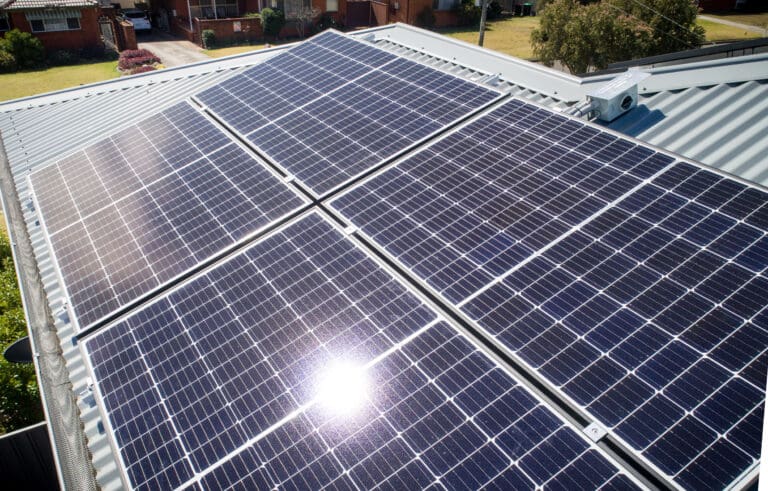
It’s getting hotter. And energy is getting expensive.
Have you spent some time searching for solutions to these two problems? Are you interested in doing your part to make the world a little greener for your kids and their kids? Do you want to save money during our current energy crisis?
Whatever your reason, you’re here and you have a question: what is solar energy?
In a time when environmental concerns in Australia and financial responsibility are at the forefront of renewable energy discussions in Australia, solar energy has stepped into the spotlight. Homes and businesses nationwide are adapting solar solutions to help reduce carbon emissions and save money on their energy bills. But what exactly is solar energy and how does it work?
At Penrith Solar Centre, we’re here to help you learn about the future of renewable energy solutions. We’re dedicated to providing Sydney, New South Wales, and further with smart, safe and reliable solar solutions. We’ve installed thousands of solar systems (panels and batteries) to reduce our customers’ grid reliance and improve their bottom line. We’re here to help you navigate this new journey into harnessing the power of the sun.
First, you’ll need to understand what it is we’re talking about so you can ultimately make informed decisions that will align with your energy needs. In this article, you will learn:
- What is Solar Energy?
- How Does Solar Energy Work?
- How Can I Use Solar Energy in My Daily Life?
- What Are the Pros and Cons of Solar Systems?
- Why Should I Get a Solar System?
That last bullet point might sound a little sales-y. We are a bit biased, but we’re going to give you our best uncompromising and straightforward answers to these questions. So grab a cuppa and sit with us for a spell as we look at what solar is and what it might mean for you.
What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is a form of renewable energy harvested from the sun’s rays by solar panels. Sunlight is converted by solar panels into electricity for several purposes; from powering your home or business to running the international space station. All the people on Earth use electricity in some capacity daily.
Most electricity used on the planet is generated from burning fossil fuels, and the carbon generated through this process pollutes the atmosphere. The polluted atmosphere is trapping radiation from the sun and causing irregular weather patterns, which is affecting everyone on the planet.
Solar panels generate electricity for many purposes in an economically sensible and environmentally conscious manner. Currently, there’s less infrastructure in solar energy on a large scale than burning fossil fuels, but it’s rapidly catching up as more homes and businesses adopt it as a source of electricity.
It has the potential to be the primary means of generating electricity worldwide. It doesn’t pollute the atmosphere, it doesn’t cause irregular weather, and the electricity generated through the process of collecting solar energy works just as well as the electricity generated by burning fossil fuels.

When we use the phrase “solar energy,” we’re actually talking about two different types of electricity: solar energy and solar power. Power and energy are not the same thing. In layman’s terms, power is electricity in motion, like when it is travelling through a cable, and energy is electricity when it’s stored up in a battery.
Add the word “solar” at the beginning of either of those words and you’re referring to electricity that was harnessed from sunshine. Solar power is electricity moving from the panels to your home, and solar energy is stored in the solar battery.
That being said, “solar energy” is a catch-all term that oftentimes is used by the solar industry (and in media reporting) to encapsulate both solar power and solar energy.
Ready to go solar? click here.
How Does Solar Energy Work?
There are a variety of components to every solar system. Most of them are similar but there are some variations in the technology depending on the brand, equipment, and design of the system.
Sunlight: The sun is 150,000,000 kilometres away, give or take a few thousand k’s. Sunlight travels from the sun to planet Earth in the form of radiation that we call sunshine. That radiation has a spectrum of characteristics, some are detectible by the human eye like colour, and some are not, like ultraviolet radiation. It’s the ultraviolet radiation that concerns us today. The ultraviolet radiation hits the solar panels on the roof of a home or business, where the panels transform it.
Panels: Solar panels are made up of individual solar cells composed of silicon semiconductors. When ultraviolet radiation (sunlight) interacts with the semiconductors, it excites the electrons in the solar cells.
On a subatomic level, the electrons circling their atoms break free from their respective orbits and become negatively charged, breaking free from their atoms like Taylor Swift belting out a power ballad about her ex-boyfriend. They leave behind a hole in the atom, causing it to become positively charged.
The free electrons follow the path of least resistance and move towards the surface of the solar cells, while the holes they left behind are pushed away from the surface. This creates a current. This is how DC (direct current) electricity is produced. That’s what the solar panels do.
Microinverter or Inverter: From this point forward, there’s some variation in how the solar system works based on what type of technology the solar system uses. If it’s a microinverter solar system, where a microinverter is mounted underneath each solar panel, then the DC electricity is converted to AC (alternating current) electricity before travelling through cabling to the home or battery.
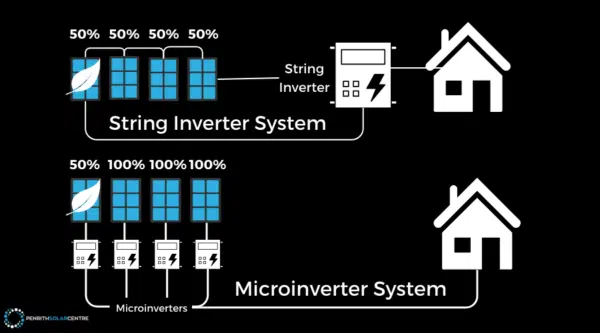
If it’s a string solar system, the DC electricity travels through cabling to a central inverter, usually located on the side of the home near the main switchboard, where it’s converted to AC electricity to power the home. This conversion from DC to AC electricity is crucial as all appliances are powered by AC electricity. For more information on the difference between microinverter solar systems and string inverter solar systems, you might want to check out the following article titled, Microinverters vs. String Inverters: An Honest Comparison.
Main Switchboard: Once the electricity is converted from DC to AC in an inverter or microinverter, it travels to the main switchboard. Like water flowing downhill, electricity will follow the path of least resistance. It will power the home and appliances within first with the excess then going to either a solar battery or to the grid for a feed-in tariff.
How Can I Use Solar Energy In My Daily Life?
Well, how do you use electricity?
Do you need light after the sun goes down? Solar energy (if you have a solar battery) can do that. Maybe it’s cold where you live, and you need some heating in your home. Solar energy (if you have a solar battery) can do that. Or if it’s hot and perhaps you’re interested in running an air conditioning? Solar energy (you guessed it — if you have a solar battery) can do that too.
There are just so many opportunities for solar energy in everyone’s day to day. The most important thing you need to consider when you’re looking into solar solutions for your lifestyle is a good honest look at your energy consumption patterns.
Before I started writing about solar systems, I rarely gave my energy usage any consideration except for the quarterly bills I received. Of course, I would do things like go around the house turning off lights, because when I was a kid, my parents would hassle me about doing exactly that to keep the energy bill low.
There are some questions you need to ask yourself about your energy consumption patterns:
- When are you home? Is the sun up? Or is it at night after the sun goes down? Are you retired or working from home?
- What types of appliances are you running? Do you use an air conditioner? What type of lighting do you have?
- What season of the year is it? How do your energy consumption patterns shift from summer to winter?
- How big is your home and how many people are in it? What are their habits and preferences?
- How many appliances are running when your home is “idling?” Idling, incidentally, is the state your home is in when certain appliances are using electricity because they’re constantly on. Things like refrigerators, pool pumps, humidifiers, or security systems.
When you start to think about it, there’s a lot to consider about what type of energy needs you have. Your energy needs will dictate what type of information you will need as you explore solar systems.
click here to start saving with solar.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Solar Systems?
Like everything, solar systems have their advantages and disadvantages. This is our best effort at representing them from an unbiased perspective.
Pros:
Environmentally Conscientious: As we touched on above, solar energy is a wonderfully environmentally friendly way of powering homes, businesses, and space stations. It’s one of the cleanest sources of energy available and the supply (sunshine) is literally limitless. Solar energy does not burn fossil fuels, so there’s no pollution. It’s the best way to limit the impacts of climate change.
Long-Term Savings: Solar systems save money long term. Period. End of story. There’s an initial upfront cost for the equipment and installation, but it generally pays itself off between 4 – 6 years, an additional year or two if you also invest in a solar battery. Once that initial cost is recouped, your energy is free. Solar systems also require little maintenance to upkeep. The panels will need cleaning from time to time. If you have a battery, you’ll want a check-up on a regular basis.
Grid Independence: If you don’t have a solar system, you’re reliant on the electrical grid. Which isn’t too terrible in sunny metropolitan Sydney. The grid rarely goes down here and when it does, it’s up again fairly quickly. However, in more rural areas or in regions where extreme weather is wreaking havoc on utility companies, grid independence is appealing. There are other reasons to abandon grid reliance.
Economic Growth and Job Creation: Solar energy is rapidly growing as an industry. As infrastructure is being built, jobs are created, and the economies of various communities will grow. There is worldwide growth in this industry.
Technology Advancements: As solar systems spread and becomes more available, innovations begin to increase. Panels and batteries will develop and evolve, as the technology becomes more advanced and efficient. They will absolutely get better at what they do, and the cost will go down as the industry advances.
Increased Property Value: A solar system is a huge selling point on a home when you sell it. How much it will increase the value of your home and property varies from situation to situation. You can certainly increase your asking price if you have a solar system on your roof. Folks buying a home are especially keen to reap the benefits of a solar system without the upfront costs of installing one.

Cons:
Weather Dependence: Because solar systems only work when the sun is shining on them, they are at the mercy of weather. In sunny regions of the world, it’s not a problem. But in places where there’s more cloud cover, the power generation can be inconsistent.
Initial Cost: As mentioned before, the initial cost for solar systems (especially systems that also have a battery) is high. Not everyone can afford a solar system, even if they finance it. Getting over that barrier can be a challenge for many, even if there are savings over the long term. Fortunately, there are still many subsidies from federal, state, and sometimes municipal governments to encourage people to install solar.
Power up your savings. click here.
Why Should I Get a Solar System?
A solar system is a solid investment in the sustainability of the human race (not to mention the benefits to your financial future). Here’s a summary of some of the key points to remember as you investigate solar systems further:
- The environmental benefits are amazing. You’ll be able to contribute to a cleaner, greener future for generations to come.
- A solar system will save you money. The return on investment starts about 4 – 6 years after installation, and you can kiss electricity bills goodbye.
- Energy independence as the grid becomes less stable due to erratic weather and the consequences of that erratic weather (fires and floods) might be necessary. We live in a world where everyone uses electricity for a variety of uses. You don’t want to be left in the dark.
- The incentives from the government help offset the initial upfront cost of a solar system.
- They’re low maintenance, requiring little upkeep besides the occasional diagnostic and keeping your panels clean from debris.
- Solar energy solutions have the potential to create infrastructure in communities. The growth in this industry is rapid and paving the way for job creation and economic growth.
- The technological advancements that will happen as a result of more people investing in solar energy are not just limited to solar system equipment. Who knows what the study of a more efficient way to create current by having electrons push each other apart might lead to? Maybe even another Taylor Swift power ballad? At Penrith Solar Centre, we’re Swifties.
It’s so important to evaluate your energy needs as you investigate solar solutions. It’s a versatile industry that you can fully customise to your specific needs.

If you’re interested in learning more about solar systems, you might want to read this article titled What Are the Benefits of a Microinverter System? Happy shopping!










